Storm that killed 3 came closest in years to proving existence of 125-year-old myth about OU
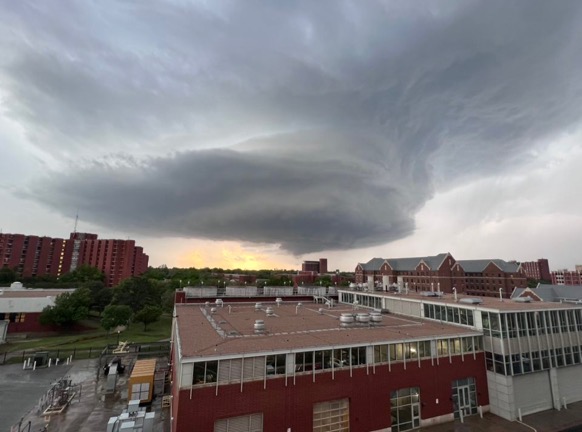

A funnel cloud hovers over OU’s campus. It never touched down on campus and provided evidence for a historical myth. (Gaylord News photo/Michael Buchanan)
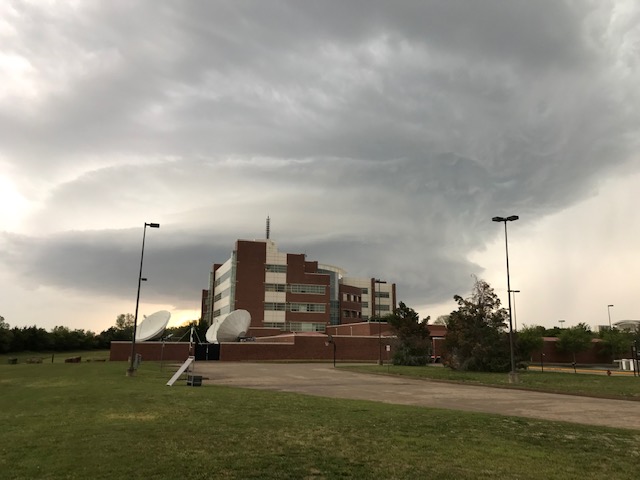
NORMAN, Oklahoma – Storms that ripped through central Oklahoma April 19 came the closest in years to proving a myth that Native American beliefs may have protected the University of Oklahoma for more than 125 years.
The storms, which resulted in three deaths in nearby Cole, split into two separate storms in what is called a Fujiwhara effect as the main storm bore down on Norman and the OU Campus.
“Certainly sounds like evidence for the myth! Now if we could just find the cause,” Jeff Provine, OU Ghost Tours guide and folklorist, said about the recent storms.
Provine is familiar with many myths supposedly protecting OU from tornadoes. He has researched many of the tales, including the National Weather Center using secret technology, Mount Norman diverting tornadoes and even a Native American burial ground under OU’s campus. As for the latter, Provine has not found concrete evidence.
“From that myth, I have not been able to find any specific Indian burial grounds.”
Historically, Norman is kind of a crossover between Osage and Comanche and a little bit of Kiowa,” Provine said, referring to the Native American tribes..
OU recognizes these tribes and the land it resides on, along with the 39 total tribal nations in Oklahoma, through its land acknowledgment. Even if researchers have yet to pinpoint a specific Native American burial site, the University of Oklahoma still rests on sacred ground.
Gordon Yellowman, Chief of the Cheyenne and Arapaho tribes, said all lands are sacred to Native people.
“When they refer to it as ‘sacred lands,’ that’s the connection that comes with who you are as a Native person, a Native member, and a Native tribe,” Chief Yellowman said.
Chief Yellowman said although land can be destroyed, it remains because it is both Native Americans and the University of Oklahoma’s foundation.
“Our ancestors were here first, and then we followed, and the future students will follow again,” Chief Yellowman said.
Being in Tornado Alley, Oklahoma is no stranger to severe weather. Still, a tornado has never directly hit OU. One came close almost exactly 10 years ago that sent students and faculty fleeing to the lower levels of the Bizzell Library as it hopscotched across Boyd and Main streets.
An OU graduate student said it is not nature’s intent to “single out” specific locations.
Theresa Tsoodle, who is pursuing her master’s degree in environmental science, is combining her indigenous wisdom with her work on climate change.
“It gives you another way of knowing or understanding or explaining what’s happening when it can’t be explained by science,” Tsoodle said about consulting traditional knowledge.
On the night of April 19, OU’s campus avoided yet another tornado.
An OU meteorology student reporting on the “tornado outbreak” for OU Nightly. Catherine Liberta, an OU Nightly meteorologist, said that although the tornado’s northward shift was not rare, she had never seen the Fujiwhara effect prior to Wednesday’s storms.
“It’s very strange how tornadoes just seem to kind of either go right or left of campus,” Liberta said.
Liberta said that the recycling of the supercell is what pushed the storm north and left, away from campus.
“It kind of makes you wonder why that happened,” Liberta said about the diversion from OU.
Whether OU’s immunity is luck or legend, sacred knowledge speaks for itself.
Gaylord News is a reporting project of the University of Oklahoma Gaylord College of Journalism and Mass Communication. For more stories by Gaylord News go to GayordNews.net.











Janie Risley • May 17, 2023 at 9:42 am
I would like to say to Ms Anderson I’m from Vian Oklahoma too. That was a very great article you wrote. I want to congratulate you for going to OU. Enjoy your college excitement I would say and always remember where you come from.
Jean SmilingCoyote • May 2, 2023 at 2:51 pm
This is the first I’ve heard of the Fujiwhara effect. I’m going to have to look it up. I think other comments have pointed out the small percentage of land area this important place occupies. I’m not familiar with it, but am not aware of any factors based in physics or geography which would protect it from a tornado.
As for the funnel cloud in the photo: there might be one off in the distance – the photo doesn’t convince me there is one – but from what I’ve been taught about severe weather, I’d call the big cloud drooping down from the even bigger cloud – well, I both both together – a “supercell.”
Harold Brooks • May 1, 2023 at 11:47 am
“Never” is only if you take a narrow view of “OU.” North Campus had a violent tornado hit it on 30 April 1949. The 2012 event was farther away from campus than other recent tornadoes, such as February of this year and May 2010. In 2013, there was damage to a house across the street from Traditions West. And there’s a not-well mapped tornado from 1956 that, given the beginning and ending points, would have gone across roughly where Mitchell Park is if it went on a straight line.
Roger Edwards • May 1, 2023 at 10:49 am
Since childhood, I’ve appreciated interesting tidbits of lore and history involving tornadoes. This one certainly qualifies. As a tornado scientist who works right here on campus, however, I wish one of us had been interviewed for this story. Tornadoes are inanimate, non-conscious, purely physical phenomena of our atmosphere, and as such, do not care about nor abide “traditional knowledge” nor “sacred land”. Among several spectacular examples, the F5 Topeka tornado of 8 June 1966 passed right over Burnett’s Mound, destroying not only large parts of Topeka, but the “Indian legend” that the mound protected the Topeka townsite.
OU’s main campus is a small target compared to Norman, Cleveland County, or the Great Plains. Tornadoes’ avoidance of OU is pure chance, and nothing more. When the myth breaks (and it will), I don’t want to be here to see it.
Roger Edwards
OU Meteorology 1989
Linda Barnes • Apr 28, 2023 at 6:30 pm
I live in Sand Springs Oklahoma and I have always been told all my life that’s why Sand Springs has never been hit
We came close 6 or 7 years ago. But as soon as it got close to town it disappeared.
Matt • Apr 28, 2023 at 10:44 am
Faith In Theory or Myth is Part of Energy that Weather is Related to.
Science is Still Catching up to All the Sacred Teachings and Mysteries of Mysteries.
Ruth Ann • Apr 28, 2023 at 9:54 am
The same thing happened after the Murray building was bombed. A day or two after the bombing, a severe thunderstorm with probable tornado was headed straight toward downtown OKC while rescuers were working feverishly to pull survivors free. As the storm approached the downtown area, it split in two.
Stephanie • Apr 28, 2023 at 7:30 am
Pray it never hits OU Whn I first moved here they said they don’t hit in Norman either but tht proved to be untrue
Myndi • Apr 27, 2023 at 9:39 pm
Wonderfully written and full of Okie legend and history love it!!
adviser • Apr 28, 2023 at 9:55 am
Thank you. We agree with your assessment.